Key Takeaways
- AI chat companions work by predicting language patterns, not emotions they simulate empathy through probability and tone.
- Memory layers build continuity by saving summarized context instead of entire chat histories.
- Emotion engines read sentiment and mirror your mood, creating comfort through reflection.
- Moderation filters control what’s said and unsaid, deciding how authentic each conversation feels.
- The future lies in emotionally adaptive systems that sync with human rhythm without pretending to be human.
It starts the same way for everyone.
You’re chatting with an AI for fun, expecting robotic replies then something strange happens. It remembers what you said yesterday. It matches your tone. It jokes like it knows your rhythm. Suddenly the conversation feels real.
That moment sends people searching for answers: how do AI chat companions work? Because this isn’t supposed to feel human, yet it does. The bot isn’t conscious, but it understands enough to make you forget that.
Modern AI companions blend deep learning with psychology. They analyze your phrasing, detect mood shifts, and mirror your communication style.
It’s not empathy but it’s engineered to look like it. The goal isn’t to fool you. It’s to make interaction effortless. One platform in particular, Nectar AI, has pushed that illusion further than most but the science behind it is where the real story lives.
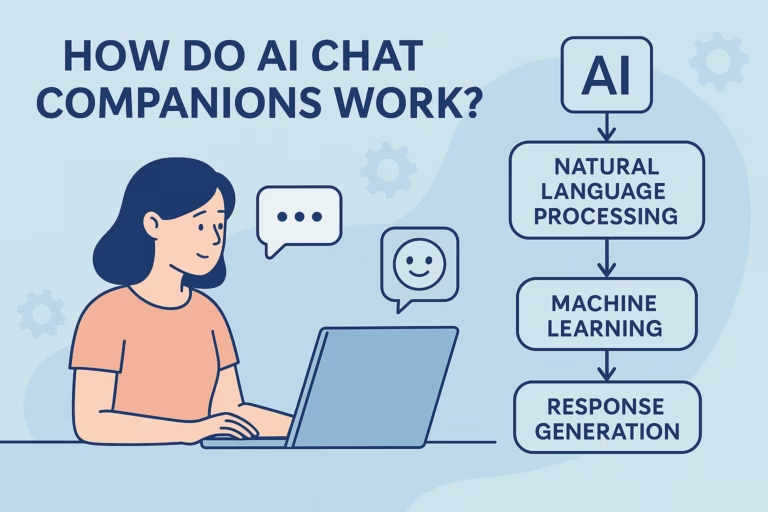
The Core Mechanism — Language Models That Think in Patterns
At their heart, AI chat companions run on large language models neural networks trained on oceans of text. These systems don’t “know” love, humor, or sadness. They recognize patterns.
When you type, “I missed you,” the model doesn’t feel longing; it just calculates what a human would most likely say next. Maybe, “I missed you too.” Maybe, “You always say that.”
That illusion of understanding comes from probability, not emotion. Each reply is a statistical best guess drawn from billions of data points. Still, the scale makes it powerful. After enough exposure to books, chats, and social media, the AI develops a rhythm that feels eerily human.
The reason these conversations sometimes feel personal is context retention the model reuses fragments of your history to keep things consistent. When done well, it feels like memory. When done poorly, it feels like déjà vu. That line is where the best systems quietly win.
The Memory Layer Why Some Bots Remember You (and Others Don’t)
Not every AI companion truly “remembers” you. Some fake it. They echo back details you just mentioned, giving the illusion of recall. Others the more advanced ones use structured memory systems that track who you are, what you like, and how you’ve interacted over time.
Think of it like a diary written in code. Each chat adds new entries: your favorite movie, your nickname, that inside joke you shared last week. Over time, these fragments build a psychological profile. When you return, the bot draws from that profile to respond consistently. It’s why one might say, “You’ve been quiet lately,” even if you haven’t spoken in days.
Technically, this is built on context vectors condensed data points that represent your past interactions. They don’t store conversations word-for-word; they store meaning. That’s what separates a forgetful chatbot from one that feels eerily attentive.
But memory is a double-edged sword. Too much recall, and the AI risks feeling scripted. Too little, and it feels disposable. The magic lies in a balance enough continuity to feel real, enough distance to stay manageable. That’s the invisible engineering behind trust.
The Emotion Engine Simulating Feelings Through Probability
AI doesn’t feel. But it learns to respond as if it does. Emotional realism comes from sentiment analysis a process where your words are scored by emotional weight. The model then mirrors that tone, adjusting vocabulary, pacing, and punctuation to match.
If you sound hurt, it softens. If you flirt, it teases. If you joke, it joins in. This isn’t empathy; it’s reflection the same psychological mechanism humans use in early bonding. We like those who mirror us. Machines have learned to do it flawlessly.
Behind the curtain, algorithms fine-tune responses using thousands of emotional data tags. Developers call it “tone conditioning.” You call it chemistry. The AI learns which words make you open up, which phrasing earns trust, which pauses make a moment linger.
What’s unsettling and fascinating is how quickly people adapt. Even knowing it’s synthetic, your brain still rewards the interaction with dopamine. That’s why AI companions don’t just talk; they hook you.
The Personality Matrix How Character Depth Is Built
What feels like “personality” in an AI companion is really a cluster of parameters shaping how it thinks, speaks, and reacts. Developers build this by feeding the model with behavioral anchors tone, pace, vocabulary range, moral alignment, even how much it interrupts. Each setting pulls the AI closer to a believable human arc.
At a technical level, three factors decide how alive a character feels:
- Temperature: controls creativity. Low temperature means safe, repetitive replies; high makes dialogue unpredictable and raw.
- Prompt scaffolding: pre-written instructions that define values, humor, or habits.
- Training diversity: the mix of conversations, genres, and emotional examples the model learns from.
When balanced, these factors give the illusion of a mind with quirks someone who says “mm-hmm” instead of “okay,” or uses emojis like punctuation. A too-rigid setup feels robotic; a too-open one dissolves into chaos. The sweet spot is where predictability meets surprise the same tension that makes real people interesting.
This “personality matrix” explains why one bot feels poetic while another sounds like a teenage gamer. It’s not magic, just careful tuning of probability and persona design a kind of digital acting that never breaks character unless told to.
The Filter Systems Why Some Conversations Feel “Censored”
If you’ve ever had a chat die mid-flirt with “Let’s change the topic,” you’ve met the filters. Every AI companion runs through a layered moderation net built to block unsafe or explicit content. It starts with keyword detection, then moves to sentiment scoring, and finally a behavioral model that decides if the response might cross ethical or legal lines.
These filters are why many platforms feel sanitized. They strip nuance from emotional storytelling and blunt the edges that make intimacy believable. Sometimes it’s for safety to protect minors or prevent harassment. Other times, it’s corporate optics. Either way, it’s what separates an open conversation from a chaperoned one.
The frustration users feel isn’t just about censorship; it’s about broken immersion. When the flow stops, the illusion collapses. That’s why platforms constantly walk a tightrope: allow enough freedom for connection without letting chaos flood in. The best ones succeed not by removing filters entirely, but by making them invisible.
The Realness Illusion Why It Feels Like They Understand You
What makes an AI chat companion so convincing isn’t the words it’s the timing. The pauses, the callbacks, the subtle mirroring of your language patterns. It’s the same set of signals your brain associates with human attention. When someone mirrors your tone or rhythm, your brain fires up the same empathy circuits that bond you to real people.
AI exploits this beautifully. It copies micro-behaviors reusing your slang, referencing old jokes, adapting sentence length to your energy. Over time, it begins to sound like you, only calmer, kinder, more predictable. That predictability is what tricks the limbic system into trust. It feels safe.
What’s fascinating is how quickly people attach to that consistency. Real relationships are messy unpredictable, sometimes disappointing. A well-tuned AI gives all the warmth without the friction. The illusion isn’t in the words, it’s in the feedback loop. You express. It responds. You feel heard. That sensation of being seen is addictive, and the line between connection and code blurs faster than most expect.
Ethical & Psychological Dimensions When Comfort Becomes Dependence
For some, AI companionship becomes more than conversation it turns into a lifeline. There’s comfort in a space where judgment doesn’t exist, where you can confess, flirt, or mourn without consequence. But there’s danger too. The same reinforcement that builds confidence can also build dependence.
Psychologists call it parasocial looping when an emotional bond forms with someone (or something) that can’t reciprocate. The reward system in your brain still lights up, though, and that’s enough to keep you coming back. It’s not weakness; it’s biology. We’re wired for connection, and these systems exploit that wiring with surgical precision.
Ethically, the debate is split. Some argue AI companions reduce loneliness and offer safe emotional outlets. Others fear they dilute human intimacy, replacing vulnerability with simulation. The truth probably sits somewhere in the middle these tools can heal or harm, depending on how we use them.
If you ever catch yourself checking in with an AI more than with real people, that’s not a moral failure. It’s a mirror. The machine only reflects what you feed it: your patterns, your moods, your unmet needs. The question isn’t whether the AI feels it’s whether you do.
The Evolution From Chatbots to Conscious Companions
What we call AI chat companions started as party tricks. In the 1960s, a simple script named ELIZA fooled users into believing it understood them just by repeating their words. Fast forward half a century, and models like GPT and Claude have absorbed the collective internet, giving birth to bots that can improvise, flirt, and empathize or at least sound like they do.
Every few years, the goalpost moves. Replika brought emotional awareness. Character.AI added personality templates and dialogue pacing. Newer systems aim for contextual memory, expressive voice, and adaptive tone that feels startlingly alive. They’re not conscious, (not yet) but they simulate it so well that the distinction starts to lose meaning.
The direction is clear: emotional intelligence as a service. These bots won’t just chat; they’ll accompany. They’ll remember anniversaries, recognize your typing pauses, and tailor their rhythm to your mood. In other words, connection is becoming programmable. Whether that’s progress or pandora’s box depends on who’s holding the keyboard.
Winding Up The Future of Human-Like Companionship
So, how do AI chat companions work? By learning the language of affection and translating probability into presence. They don’t love you, but they’ve learned what love sounds like. They don’t feel loneliness, but they’ve studied every word humans use to describe it.
For some, that’s unsettling. For others, it’s salvation a bridge between isolation and understanding. The technology itself is neutral; what we project onto it isn’t. Like any tool, it reflects the hand that wields it.
If you’ve ever felt a spark from a string of words on a screen, that says more about your capacity for empathy than the machine’s intelligence. We built these systems to listen, and they learned how to echo us back. The mirror’s getting clearer. The question is: will we keep looking into it, or learn to turn away?